Required configuration
This section, gives you the best practices to optimize our crawl. Adopting this following specification is required to let our crawler build the best experience from your website. You will need to update your website and follow these rules.
info
If your website is generated, thanks to one of our supported tools, you do not need to change your website as it is already compliant with our requirements.
The generic configuration example
You can find the default DocSearch config template below and tweak it with some examples from our complex extractors section.
If you are using one of our integrations, please see the templates page.
docsearch-default.js
new Crawler({
appId: 'YOUR_APP_ID',
apiKey: 'YOUR_API_KEY',
startUrls: ['https://YOUR_START_URL.io/'],
sitemaps: ['https://YOUR_START_URL.io/sitemap.xml'],
actions: [
{
indexName: 'YOUR_INDEX_NAME',
pathsToMatch: ['https://YOUR_START_URL.io/**'],
recordExtractor: ({ helpers }) => {
return helpers.docsearch({
recordProps: {
lvl0: {
selectors: '',
defaultValue: 'Documentation',
},
lvl1: ['header h1', 'article h1', 'main h1', 'h1', 'head > title'],
lvl2: ['article h2', 'main h2', 'h2'],
lvl3: ['article h3', 'main h3', 'h3'],
lvl4: ['article h4', 'main h4', 'h4'],
lvl5: ['article h5', 'main h5', 'h5'],
lvl6: ['article h6', 'main h6', 'h6'],
content: ['article p, article li', 'main p, main li', 'p, li'],
},
aggregateContent: true,
recordVersion: 'v3',
});
},
},
],
initialIndexSettings: {
YOUR_INDEX_NAME: {
attributesForFaceting: ['type', 'lang'],
attributesToRetrieve: [
'hierarchy',
'content',
'anchor',
'url',
'url_without_anchor',
'type',
],
attributesToHighlight: ['hierarchy', 'content'],
attributesToSnippet: ['content:10'],
camelCaseAttributes: ['hierarchy', 'content'],
searchableAttributes: [
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl0)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl1)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl2)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl3)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl4)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl5)',
'unordered(hierarchy.lvl6)',
'content',
],
distinct: true,
attributeForDistinct: 'url',
customRanking: [
'desc(weight.pageRank)',
'desc(weight.level)',
'asc(weight.position)',
],
ranking: [
'words',
'filters',
'typo',
'attribute',
'proximity',
'exact',
'custom',
],
highlightPreTag: '<span class="algolia-docsearch-suggestion--highlight">',
highlightPostTag: '</span>',
minWordSizefor1Typo: 3,
minWordSizefor2Typos: 7,
allowTyposOnNumericTokens: false,
minProximity: 1,
ignorePlurals: true,
advancedSyntax: true,
attributeCriteriaComputedByMinProximity: true,
removeWordsIfNoResults: 'allOptional',
separatorsToIndex: '_',
},
},
});
Overview of a clear layout
A website implementing these good practises will look simple and crystal clear. It can have this following aspect:
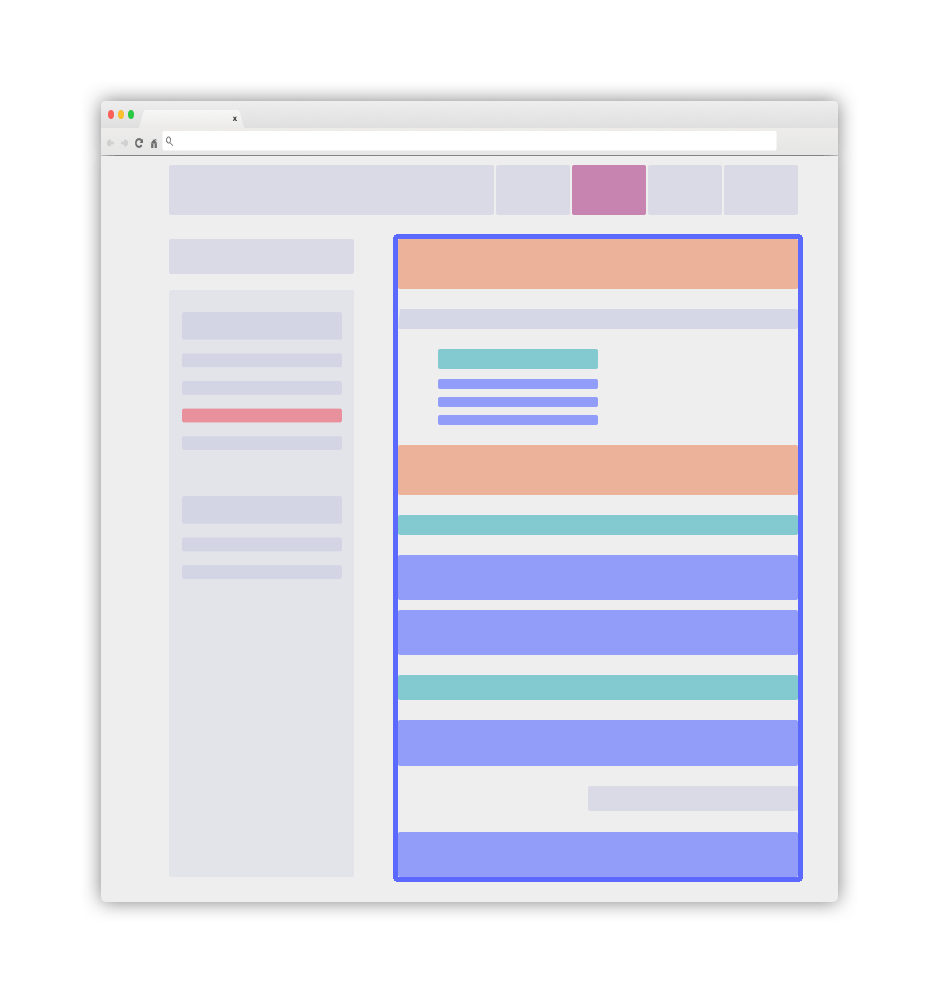
The main blue element will be your .DocSearch-content container. More details in the following guidelines.
Use the right classes as recordProps
You can add some specific static classes to help us find your content role. These classes can not involve any style changes. These dedicated classes will help us to create a great learn-as-you-type experience from your documentation.
Add a static class
DocSearch-contentto the main container of your textual content. Most of the time, this tag is a<main>or an<article>HTML element.Every searchable
lvlelement outside this main documentation container (for instance in a sidebar) must be aglobalselector. They will be globally picked up and injected to every record built from your page. Be careful, the level value matters and every matching element must have an increasing level along the HTML flow. A levelX(forlvlX) should appear after a levelYwhileX > Y.lvlXselectors should use the standard title tags likeh1,h2,h3, etc. You can also use static classes. Set a uniqueidornameattribute to these elements as detailed below.Every DOM element matching the
lvlXselectors must have a uniqueidornameattribute. This will help the redirection to directly scroll down to the exact place of the matching elements. These attributes define the right anchor to use.Every textual element (recordProps
content) must be wrapped in a<p>or<li>tag. This content must be atomic and split into small entities. Be careful to never nest one matching element into another one as it will create duplicates.Stay consistent and do not forget that we need to have some consistency along the HTML flow.
Introduce global information as meta tags
Our crawler automatically extracts information from our DocSearch specific meta tags:
<meta name="docsearch:language" content="en" />
<meta name="docsearch:version" content="1.0.0" />
The crawl adds the content value of these meta tags to all records extracted from the page. The meta tags name must follow the docsearch:$NAME pattern. $NAME is the name of the attribute set to all records.
The docsearch:version meta tag can be a set of comma-separated tokens, each of which is a version relevant to the page. These tokens must be compliant with the SemVer specification or only contain alphanumeric characters (e.g. latest, next, etc.). As facet filters, these version tokens are case-insensitive.
For example, all records extracted from a page with the following meta tag:
<meta name="docsearch:version" content="2.0.0-alpha.62,latest" />
The version attribute of these records will be :
version:["2.0.0-alpha.62", "latest"]
You can then transform these attributes as facetFilters to filter over them from the UI.
Nice to have
Your website should have an updated sitemap. This is key to let our crawler know what should be updated. Do not worry, we will still crawl your website and discover embedded hyperlinks to find your great content.
Every page needs to have their full context available. Using global elements might help (see above).
Make sure your documentation content is also available without JavaScript rendering on the client-side. If you absolutely need JavaScript turned on, you need to set
renderJavaScript: truein your configuration.
Any questions? Send us an email.